
What Does Tooth Pain While Eating Mean?
Tooth pain while eating is a feeling of discomfort, tingling, or aching that appears only when you chew food or press on the tooth, or becomes noticeably worse at those times. It may be mild and short-lived with cold or hot foods, or sharp and persistent with every bite. This type of pain is often caused by tooth sensitivity, deep dental caries (cavities), pulp inflammation, or problems in the gums or jawbone, which make the teeth more sensitive to pressure and temperature changes.
Pain when chewing is usually a warning sign that there is a problem affecting the tooth structure or the surrounding tissues, such as enamel erosion, a hairline (micro) crack, an ill-fitting filling, or inflammation around the tooth roots. Ignoring tooth pain while eating can worsen the underlying problem and lead to more complex complications, so it’s important to see a dentist to identify the exact cause and plan appropriate treatment.

Why Does Tooth Pain Occur When Chewing or Biting?
Tooth pain when eating or when putting pressure on a molar usually points to an issue in the tooth itself or in the surrounding gum tissue. It may be due to deep decay approaching the dental pulp (tooth nerve), or a small crack in the tooth that isn’t visible to the naked eye but causes sharp pain when you bite down. Gum inflammation (gingivitis) or inflammation of the periodontal ligament around the root of the tooth can also directly cause pain while chewing, especially if there is swelling or redness in the gums.
In many cases, an old filling or a crown that doesn’t fit properly can increase the pressure on certain teeth during eating, causing localized pain when chewing or biting. You also shouldn’t overlook the possibility of pulpitis (nerve inflammation) or a dental abscess, where the pain worsens with pressure on the tooth or when eating hard foods. For these reasons, the appearance of tooth pain while eating is a warning sign that requires a dental visit for early diagnosis and prevention of more serious problems.
Common Causes of Tooth Pain While Eating
Dental Caries (Tooth Decay)
Tooth decay is one of the most common causes of tooth pain during eating, especially when consuming sweets, acidic foods, or cold items. Decay occurs when bacteria attack the enamel and create a cavity, exposing the more sensitive inner layers of the tooth to external stimuli. As decay progresses, pain becomes more intense with chewing or pressure on the tooth and may present as sudden sharp stabs or a constant ache while eating.
Good oral hygiene, cutting down on sugar intake, and regular dental checkups help detect cavities early and treat tooth pain while eating before it becomes severe.
Enamel Erosion
Enamel erosion is a “hidden” cause of tooth pain during eating, because thinning or loss of enamel exposes the sensitive underlying layer known as dentin. Enamel can erode due to frequent consumption of acidic foods and drinks, brushing too hard, or using an unsuitable toothpaste.
When enamel is worn down, patients often experience sharp sensitivity or pain with cold, hot, or sweet foods, and sometimes only when chewing. Preventing enamel erosion, using a toothpaste formulated for sensitive teeth, and seeing a dentist regularly can significantly reduce pain while eating and improve overall oral comfort.
Read more about: Enamel erosion

Pulp Inflammation (Pulpitis)
Pulp inflammation (pulpitis) is a common reason for severe tooth pain while eating, especially when pressure is applied to the tooth during chewing. It develops when deep decay or trauma extends into the pulp, which contains the tooth’s nerves and blood vessels, resulting in intense pain that may continue even without eating.
Patients often describe pulpitis as a throbbing or constant pain that worsens with hot or cold foods and may be strong enough to wake them at night. Pulpitis typically requires definitive treatment such as root canal therapy to save the tooth, relieve pain while eating, and prevent complications like a dental abscess.
You may also be interested in: How to relieve and treat tooth nerve pain
Gum Inflammation or Gum Recession
Gum disease and gum recession both contribute to tooth pain while eating. Inflammation of the supporting tissues around the teeth weakens tooth stability and increases sensitivity in the area. Gingivitis is usually caused by plaque and tartar buildup, leading to redness, bleeding, and bad breath; patients may feel pain when chewing or when food touches the inflamed gums.
Gum recession, on the other hand, exposes the tooth roots, which are naturally more sensitive. This often leads to pain when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods, or when applying pressure to the tooth. Professional cleaning, improved daily oral care, and early treatment of gum disease can greatly reduce pain while eating and help maintain healthy gums.
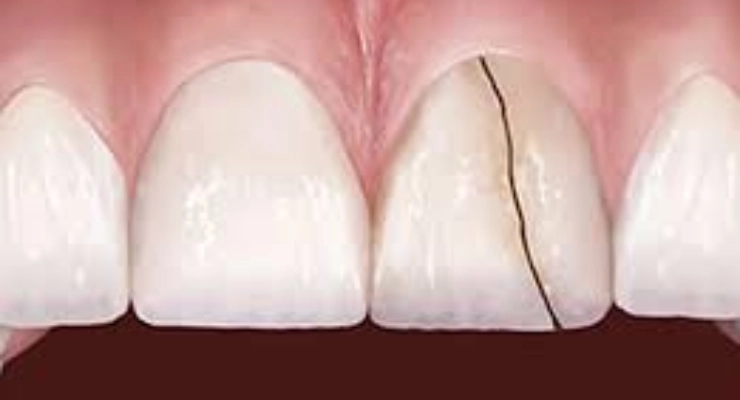
Tooth Fracture or Cracked Tooth
A broken or cracked tooth is a direct cause of tooth pain during eating, especially when biting hard foods such as nuts, bones, or hard candies. The fracture may be obvious and visible, or it may be a fine (hairline) crack that you cannot see but still causes sharp pain when chewing or when pressure is applied to a specific point on the tooth.
A crack creates a pathway for bacteria and temperature changes to reach the inner layers of the tooth, increasing sensitivity and pain while eating. Early diagnosis of a cracked or fractured tooth by a dentist, followed by appropriate restoration with fillings or crowns, can protect the tooth and help prevent worsening pain or eventual tooth loss.
Improper Fillings or Crowns
Ill-fitting dental fillings or crowns can directly cause pain while eating, even if the original decay has been treated. If a filling is too high or not shaped correctly, it can cause discomfort when chewing and place excessive pressure on the tooth or the opposing teeth.
Similarly, poorly sealed crowns may allow bacteria and food debris to slip underneath, leading to gum inflammation or pulp involvement and triggering pain while eating. Adjusting the bite, reshaping the filling, or replacing a faulty crown—along with regular dental follow-up—is essential to eliminate pain during eating and ensure that restorations are stable and functional.
Tooth Pain with Hot or Cold Foods
Tooth pain when consuming hot or cold foods and drinks is one of the most common symptoms of tooth sensitivity. This typically occurs due to enamel erosion or gum recession that exposes the underlying dentin, which contains microscopic tubules connected to the tooth nerve. When the nerves are exposed or irritated, a person may feel sudden, sharp pain when drinking cold beverages like iced water or juice, or when eating or drinking hot items such as soup or coffee.
Sometimes this type of sensitivity can signal cavities, microcracks in the tooth, pulp inflammation, or overbrushing with excessive force or a hard-bristled brush. Ignoring tooth pain with hot or cold foods may allow the problem to progress, potentially causing severe inflammation or a dental abscess. If sensitivity persists, you should see a dentist for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan, which may include desensitizing toothpaste, fluoride treatments, restorations, or root canal therapy depending on the cause.
Understanding why tooth pain occurs when eating—especially with hot or cold foods—helps in early prevention and protects the teeth from future complications.
Tooth Pain with Hard Foods or While Chewing
Tooth pain when eating hard foods or during chewing is a common sign that often points to deep decay, pulp inflammation, or a fine crack in the tooth structure that isn’t visible to the naked eye. When you bite down, especially on hard foods like nuts or crusty bread, the increased pressure on the tooth, pulp, and surrounding tissues can trigger sharp or throbbing pain.
This type of pain may also be related to gum disease, tooth sensitivity, or an old, leaking filling that allows bacteria and food particles to penetrate. Neglecting this pain can allow the inflammation to extend into the bone surrounding the tooth root, making treatment more difficult later. If you frequently feel pain with hard foods or when pressing on a tooth, it’s important to see a dentist promptly to identify the cause and start proper treatment before the condition worsens.

Is Tooth Pain While Eating a Sign of Something Serious?
Tooth pain during eating is not a minor symptom to be dismissed. It can be an early indicator of conditions that need timely intervention, such as deep dental caries, pulp inflammation, enamel erosion, tooth cracks, or gum disease. Sharp pain when chewing or when eating cold, hot, or sweet foods usually means that the inner sensitive layers of the tooth have become exposed or inflamed.
Ignoring this pain may lead to complications such as gum abscesses or irreversible nerve damage, which can require more complex treatment like root canal therapy or even tooth extraction. Pain while chewing should therefore be taken as a warning sign that requires a dental visit as soon as possible to determine the cause and plan appropriate treatment, rather than relying on painkillers that only mask the problem. This approach helps preserve the health of your teeth and gums and prevents serious complications that can affect your ability to eat, speak, and maintain a good quality of life.
How Is the Cause of Tooth Pain While Eating Diagnosed?
Diagnosing the cause of tooth pain while eating starts with a detailed medical and dental history. The dentist will ask about the type of pain, when it occurs, and whether it worsens with cold, hot, or sweet foods, or with pressure on a particular tooth. The dentist then performs a thorough examination of the teeth, gums, and oral cavity to look for decay, fine cracks, gum inflammation, gum recession, or faulty fillings and crowns that may be causing pain while chewing.
In most cases, the dentist will use a special instrument to apply gentle pressure on each tooth to pinpoint the source of pain. Dental X‑rays are often ordered to detect deep decay, pulp inflammation, abscesses, or root problems that are not visible clinically. In some situations, thermal sensitivity tests may be performed by applying cold or hot stimuli to the tooth to assess the pulp response.
These diagnostic steps help distinguish the exact cause of pain while eating and determine whether the tooth needs root canal therapy, a simple filling, or periodontal treatment. Accurate diagnosis is the foundation for choosing the best treatment plan and eliminating tooth pain during eating safely and effectively.
Treatment Options for Tooth Pain While Eating
Root Canal Treatment (Endodontic Therapy)
When tooth pain while eating is accompanied by deep, throbbing pain, the cause is often pulp inflammation, and root canal therapy becomes the most effective solution. In this procedure, the dentist cleans the root canals, removes the inflamed or infected pulp tissue, then disinfects and fills the canals with specialized materials to prevent bacterial reinfection.
Root canal treatment relieves pain during chewing and preserves the natural tooth instead of extracting it, especially when decay has reached the pulp. If pulpitis is left untreated, it may lead to a dental abscess, facial swelling, and more intense pain with chewing or pressure. Root canal therapy is therefore a key treatment for controlling tooth pain while eating and preventing serious complications.
Treatment of Gum Problems
Gum problems such as gingivitis and periodontitis (inflammation of the supporting tissues around the teeth) are common causes of tooth pain while eating, particularly during chewing or when pressure is applied to the teeth. Treatment begins with accurate diagnosis, followed by professional deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar that cause inflammation and sensitivity.
The dentist may prescribe a therapeutic mouthwash and, in some cases, antibiotics, along with detailed instructions for daily oral hygiene to help reduce pain during eating. Improving gum health reduces tooth mobility and sensitivity, which in turn decreases pain during chewing and allows patients to eat more comfortably and safely.

Adjusting or Replacing Fillings and Crowns
In many cases, tooth pain while eating is caused by an old high filling or an ill-fitting crown that places excessive pressure on the tooth or neighboring teeth during chewing. The dentist will check the bite (how the teeth come together when closing and chewing) and then adjust the height or shape of the filling or crown, or replace it entirely if it is damaged or leaking.
Improper restorations can lead to significant sensitivity and sharp pain while eating, particularly with hard foods or when pressure is applied to a specific point. Accurate adjustment of fillings and crowns is therefore essential in treating tooth pain during eating, helping to distribute chewing forces evenly and protecting the tooth from cracks or fractures.
Using Mouthguards in Certain Cases
Sometimes, tooth pain while eating is not just due to decay, but also related to bruxism (teeth grinding) at night or excessive clenching while chewing. In such cases, using a custom-made night guard or sports mouthguard is often recommended. These devices are designed to protect the teeth from excessive friction and impact.
A mouthguard helps reduce pressure on the teeth, gums, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which decreases chewing-related pain and sensitivity while eating. Using mouthguards, along with treating associated problems such as decay or pulp inflammation, forms part of a comprehensive plan to manage tooth pain during eating and prevent future enamel wear or tooth cracks.
Can Tooth Pain While Eating Be Relieved at Home?
In many situations, you can temporarily relieve tooth pain while eating at home until you’re able to see a dentist, especially if the pain is due to mild sensitivity or minor gum inflammation. Avoiding very hard foods and extremely hot or cold items can reduce irritation to the tooth nerve. It is also advisable to cut down on sticky sweets and sugary snacks that promote decay and intensify pain while chewing.
Using a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth can help lessen discomfort, and rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash or warm salt water may help reduce gum inflammation and swelling around the tooth. Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used safely according to the recommended dosage, but you should never place painkiller tablets directly on the gums, as they can cause chemical burns.
These home measures only provide temporary relief. Persistent or worsening pain while eating usually indicates a deeper problem such as extensive decay, pulp inflammation, a cracked tooth, or gum disease. In such cases, you need to see a dentist promptly to diagnose and treat the underlying cause before the condition progresses.
How to Prevent Tooth Pain While Eating
Preventing tooth pain during eating starts with maintaining good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth twice daily with a fluoride toothpaste and use dental floss to clean between the teeth, where food debris and bacteria tend to accumulate and can cause cavities and sensitivity.
Limiting sugary and acidic foods and beverages—such as soft drinks, packaged juices, and sticky sweets—helps protect enamel and reduce tooth sensitivity while chewing. Using toothpaste formulated for sensitive teeth and a fluoride mouthwash can strengthen enamel and shield the tooth nerves from external stimuli.
Avoid biting very hard objects like ice and hard nuts, as they can create tiny cracks in the teeth that later cause pain during eating. Early treatment of dental problems such as cavities, gum disease, and enamel erosion through regular checkups every six months is essential for preventing tooth pain while eating and maintaining long-term oral health.

When Should You See a Dentist Immediately?
Tooth pain while eating can be a sign of serious issues such as deep decay, pulp inflammation, an abscess, or an invisible crack in a molar. You should seek urgent dental care if the pain lasts more than two days, becomes severe when chewing or pressing on the tooth, or is accompanied by gum or facial swelling, difficulty opening your mouth or swallowing, or fever.
Ignoring tooth pain while eating can allow infection to spread to the pulp or the bone surrounding the tooth, increasing the likelihood of needing complex treatments such as root canal therapy or even extraction. If you notice intense sensitivity with hot or cold foods, sudden pain when biting hard foods, or discharge of pus or foul odor from the mouth, don’t wait for the pain to go away on its own. Schedule an urgent appointment with your dentist to diagnose and treat the cause early and protect your oral health.
The Role of Batal Dental Clinic in Diagnosing and Treating Tooth Pain
At Batal Dental Clinic, managing tooth pain while eating starts with an accurate diagnosis based on a comprehensive clinical examination, dental X‑rays, and, when necessary, 3D imaging to determine the exact cause of pain—such as deep cavities, pulp inflammation, tooth sensitivity, gum disease, or tooth fractures. The dentists take the time to listen to the details of your complaint, including the location of the pain, when it occurs, and whether it worsens with hot, cold, or when chewing, which helps distinguish between different types of tooth pain.
After diagnosis, Batal Dental Clinic provides a personalized treatment plan that may include aesthetic fillings, advanced root canal therapy, crowns for weakened teeth, or periodontal treatment. Modern techniques are used to minimize discomfort and make the experience as comfortable as possible. The clinical team also offers preventive guidance after treatment, including proper brushing and flossing techniques, choosing the right toothpaste for sensitive teeth, and dietary tips to reduce episodes of tooth pain while eating and prevent recurrence in the future.
Patient Guide: Frequently Asked Questions About Tooth Pain While Eating
What causes tooth pain while eating?
Tooth pain while eating is most often caused by tooth decay, pulp inflammation, enamel erosion, gum disease, or a tooth fracture. Chewing pressure irritates the tooth’s nerve and surrounding tissues, triggering pain.
Does tooth decay cause pain only when eating?
Yes. In the early stages, decay may cause pain only during eating, especially with sugary or cold foods, before the pain becomes more frequent or constant.
Why does my tooth hurt when I chew hard food?
This may be due to a fine crack in the tooth, a high filling, or pulp inflammation, all of which make pressure during chewing painful.
Does tooth pain while eating always mean I need a root canal?
Not always. It depends on how severe the inflammation is and whether decay has reached the pulp. Your dentist will determine the appropriate treatment after examination and necessary tests.
Can I treat tooth pain while eating at home?
You can relieve the pain temporarily with over-the-counter pain relievers and by avoiding hard foods, but definitive treatment requires a dental visit to address the underlying cause.
When should I see a dentist immediately?

If the pain persists or worsens, or if there is swelling, bleeding, difficulty chewing, or other concerning symptoms, you should see a dentist right away to prevent complications.

